Corrosion Performance of Ni and Ni-P Coatings via Electrodeposition in an Emulsified Supercritical CO2 bath
Sung-Ting Chung, Yan-Chi Chuang, Cheng-Yu Li, Shih-Yi Chiu, Wen-Ta Tsai*
* E-mail : wttsai@mail.ncku.edu.tw
Department of Materials Science and Engineering National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan
报告人:蔡文达
个人简介:
台湾台南市成功大学特聘教授 ,历年来执行数十项腐蚀相关研究课题,研究成果总计已有215篇学术期刊论文发表,其中有SCI论文166篇;而国内外学术研讨会发表的论文超过285篇,已获得国内外核准的专利有10件,其它技术报告已超过120件。
曾任两届防蚀工程学会理事长,主办第九届亚太腐蚀控制会议,参与海峡两岸材料腐蚀防护研讨会的举办,为推动海峡两岸腐蚀专业的交流与合作做出巨大贡献。

NCKU: National Cheng Kung University
- Founded: 1931
- Area : 183 hectares
- Colleges: 9
- Departments: 40
- Institutes: 51
- Personnel : 5084
- Faculty : 1278
- Staff : 1531
- Affiliated Hospital : 2275
- Enrollment : 21889
- Undergraduate : 11056
- Master : 7417
- Doctoral : 3416

Background information
Properties and applications of nickel (Ni) deposition
Properties: Electrical conductivity, Corrosion resistance, …etc.
Applications: Electronic packaging, MEMS, advanced integrated circuit (IC), Anti-corrosion, Anti-wear, Decoration…etc.

Methods of nickel (Ni) deposition
Dry Process
- PVD
- CVD
- Sputter…etc.
Wet Process
- Electroplating
- Electroless plating…etc.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Wet Process
Advantages :
Cheap
Easy to operate
High deposition rate…etc
Disadvantages:
The formation of hydrogen may create several pin-holes on the film.
Wastewater treatment (toxic species)…etc
Possible solutions:
Non-aqueous or green electrolytes:
ionic liquids and supercritical CO2…etc
#p#副标题#e#
Supercritical Fluids
Characteristics of CO2
CO2 Phase Diagram

Critical properties of various solvents

Characteristic of CO2 : Gas, Supercritical Fluid and Liquid
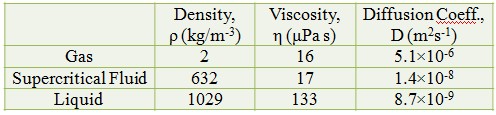
Gas-like Diffusivity
Liquid-like Density
Low Surface Tension
New Technology for Electrodeposition
Supercritical Nano-Plating (SNP)
Sone and colleagues have demonstrated the electrodeposition of nickel from an emulsion of an aqueous nickel plating solution in sc-CO2 bath.

Nonionic surfactant : PEO-PPO (6 wt.%)
sc-CO2 volume fraction vs. Current efficiency & Resistance


The result indicates that the plating electrolyte can be reduced at 60% compared to that of currently industrially by used plating bath.#p#副标题#e#
The plated films using this method have a uniformity of surface and the grain size is smaller than that formed by using conventional electroplating methods.
Experimental Conditions for Electrodeposition
Substrate
• Brass substrate cut in2.4 × 1 cm2×2
• Polish in a slurry containing 0.3 μm Al2O3 powder

* Modified Watt’s bath including NiSO4·6H2O, NiCl2·6H2O and H3BO3
Plating condition
• Current density: 5 A/dm2 for Ni and Ni-Al2O3 deposits
2 A/dm2 for Ni-P alloy coatings
• Temperature : 50oC
• Total charge : 108 coul.
• Aqueous electrolyte : 0.1 MPa (air), 10 MPa (Ar)
• Electrolyte containing CO2 fluid: 5 MPa, 10 MPa and 15 MPa
Heat-treatment
The heat-treatment of Ni-P alloy coatings was performed from room temperature to heat-treated temperature for 1 hr. (350, 400, 450, 500, and 550oC)
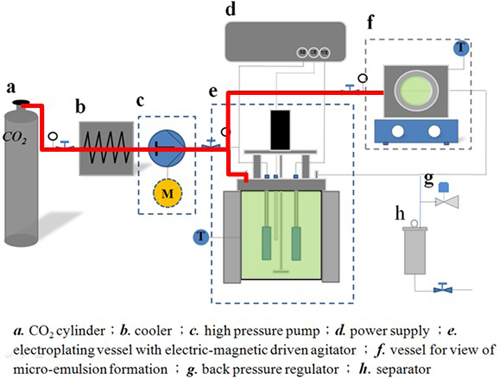
Experimental Apparatus for Electrodeposition
Materials Characterization for Electrodeposits

Experimental (I) Pure Ni deposits
Material Characterization (Ni Electrodeposit)
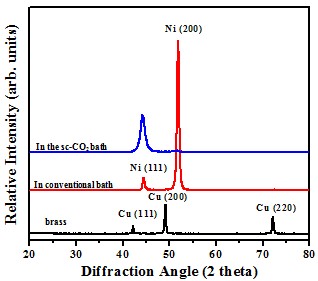
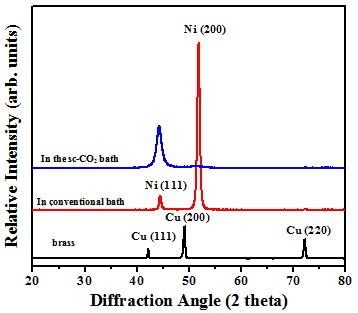
Crystal structure
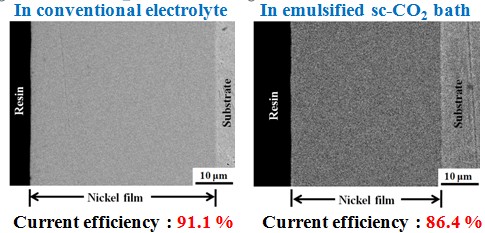
Current efficiency
Surface roughness
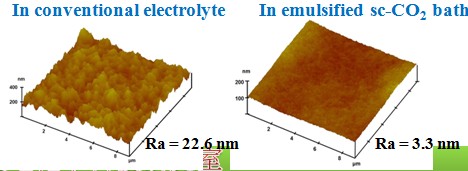
Chemical composition(effect of sc-CO2 fluid)#p#副标题#e#
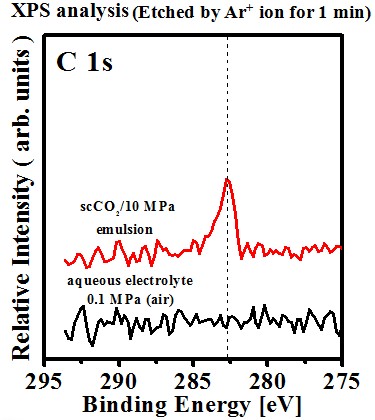
Chemical shift
- C(graphite) : 284.6 eV
- C dissolved in Ni lattice
C(Ni-C) : 282.8 eV
Possible reactions responsible for the formation of Ni-C deposit:
Ni2+ + 2e- à Ni
2H+ + 2e- à H2
HCO3- + 5H+ + 4e- → C + 3H2O
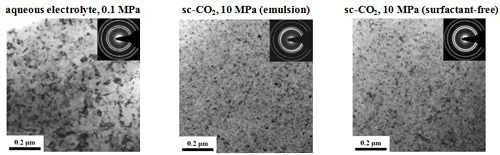
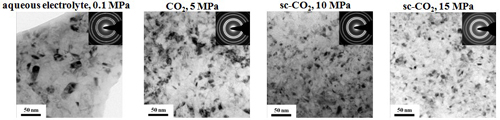
Microstructure and Micro-hardness
TEM microstructure
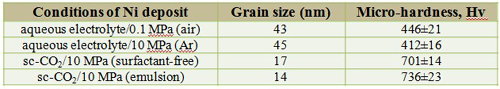
Grain size and micro-hardness
Electrochemical behavior
Potentiodynamic polarization curve
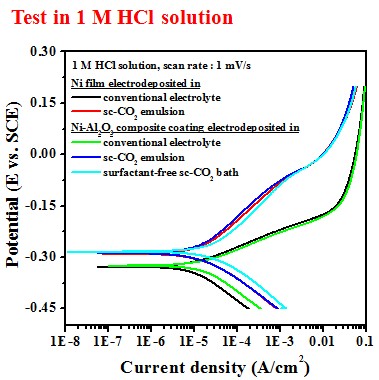
Test in 1 M HCl solution

EIS result

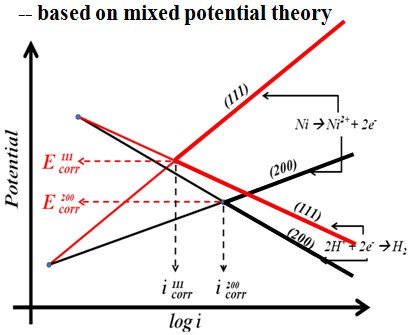
Electrochemical behavior (effect of crystallographical orientation)#p#副标题#e#
Crystal structure
Schematic diagram
Microstructure and Micro-hardness
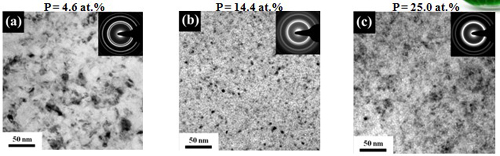
(effect of CO2 pressure)
TEM microstructure
Grain size and micro-hardnes

The dependence of micro-hardness on the grain size is also revealed
Hall-Petch equation σy = σo + kyd-1/2
Electrochemical behavior
-- Potentiodyamic polarization curve
Test in 1 M HCl solution

Experimental (II) Ni-Al2O3 composite coatings
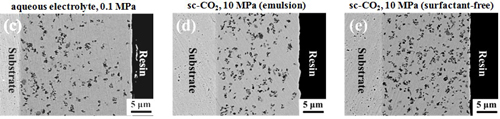
Surface morphology and cross section micrograph
(electrolyte containing 10 g/L Al2O3)
Surface morphology

Cross section micrograph
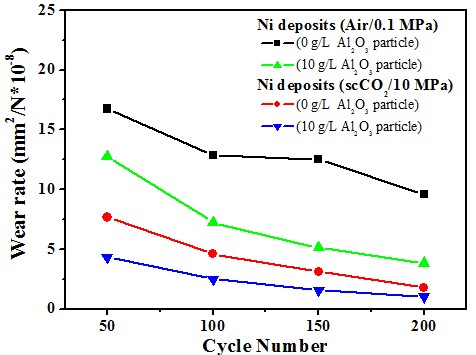
Micro-hardness & Wear rate (electrolyte containing 10 g/L Al2O3)
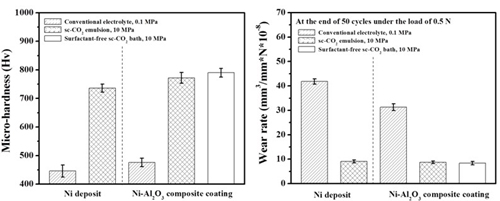
Ni/Al2O3 deposits
Wear resistance#p#副标题#e#
Ni-P/Al2O3 deposits
Wear resistance

Electrochemical behavior (electrolyte containing 10 g/L Al2O3)
-- Potentiodyamic polarization curve
Surface morphology and cross section micrograph (electrolyte containing 10 g/L SiC)
Surface morphology
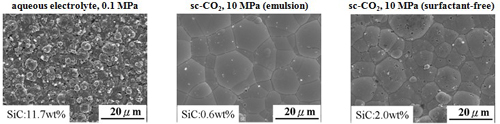
Cross section micrograph

Micro-hardness & Wear rate(electrolyte containing 10 g/L SiC)
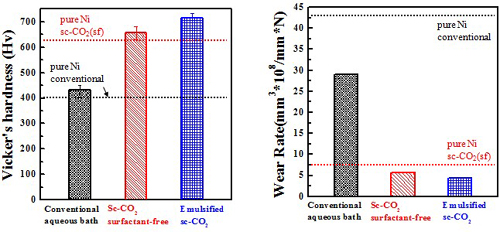
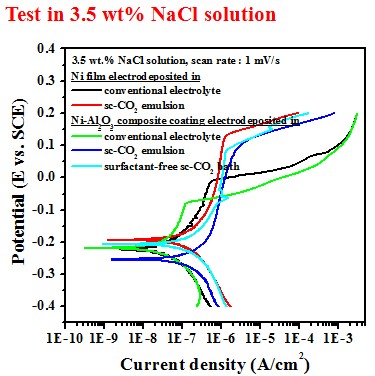
Electrochemical behavior (electrolyte containing 10 g/L SiC)#p#副标题#e#
Test in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution

Electrochemical behavior
Schematic diagrams

Experimental (III) Ni-P alloy coatings
P content effect of [H3PO3]

The co-deposition mechanism for the Ni-P alloy coatings
Ni2+ + 2e- à Ni
6H+ + 6e- à 6Hads
Direct mechanism:
H3PO3 + 3H+ + 3e- à P + 3H2O
Indirect mechanism:
H3PO3 +6Hads à PH3 + 3H2O
2PH3 + 3Ni2+ à 3Ni + 2P + 6H+
Grain size (effect of P content)
In conventional electrolyte
In emulsified sc-CO2 bath

Hardness effect of grain size

Hall-Petch equation
Grain size > 10 nm
σy = σo + kyd-1/2
Inverse Hall-Petch equation#p#副标题#e#
Grain size < 10 nm
σy = σo - kyd-1/2
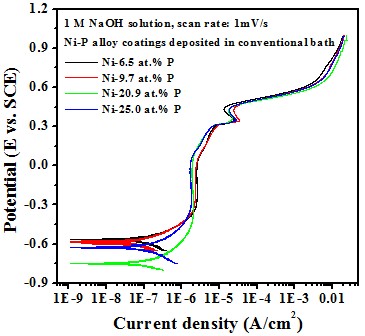
Electrochemical behavior effect of P content
-- Potentiodyamic polarization curve
Test in 1 M NaOH solution

(Test in 1 M HCl solution)
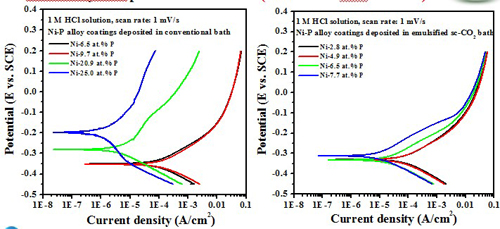
The formation of an adsorbed film of hypophosphite (H2PO2-) generated by the oxidation of phosphorus present in the coating surface, which in turn blocks the water molecules from interacting with nickel, thus inhibiting nickel oxidation.
Electrochemical behavior effect of heat treatment
Test in 1 M HCl solution

Conclusions
The Ni-based deposits could be successfully fabricated from an emulsified sc-CO2 bath.
The surfactant addition in sc-CO2 containing electrolyte play an important role on the surface appearance of the deposits. When electrodeposition was performed in the emulsified sc-CO2 electrolyte, a flat and almost pinhole-free surface was observed.
Carburization of metal can be achieved by electrodeposition in the sc-CO2 -containing baths. As a result, the hardness of Ni-based films deposited in the sc-CO2 bath was enhanced by the additional solid solution strengthening mechanism.

In 1 M HCl solution, the Ni film deposited in sc-CO2 bath had a lower anodic current density and a higher polarization resistance, which is mainly attributed to the crystallographical orientation.
The high P content in the deposit was beneficial to enhance the corrosion resistance of the Ni-P alloy coating, in 1 M HCl solution.
Heat treatment significantly enhances the hardness and corrosion resistance compared to the as-deposited Ni-P alloy.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the National Science Council of the Republic of China under Contract No. NSC 98-2622-E-006-032 for partially supporting the use of instruments for surface characterization.

官方微信
《中国腐蚀与防护网电子期刊》征订启事
- 投稿联系:编辑部
- 电话:010-62313558-806
- 邮箱:fsfhzy666@163.com
- 中国腐蚀与防护网官方QQ群:140808414





