1 辐照对IASCC行为的影响规律
为屈服强度,η为应力强度因子K拟合系数。
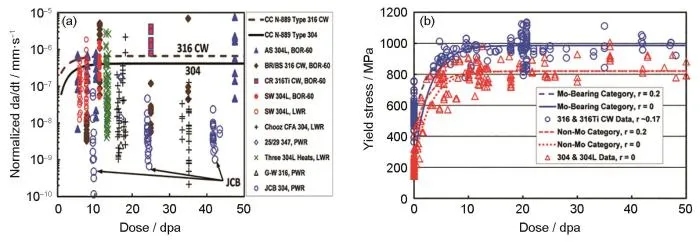
图1 IASCC数据中CGR与屈服应力的剂量依赖性[15]
Fig.1 Dose dependence of CGR and yield stress in IASCC datas[15]: (a) CGR versus dose plateau behavior of JCB and earlier IASCC data, (b) Irradiated yield stress model and data at 288 ℃ for cold-worked types 316 and 316Ti and types 304 and 304 L stainless steel
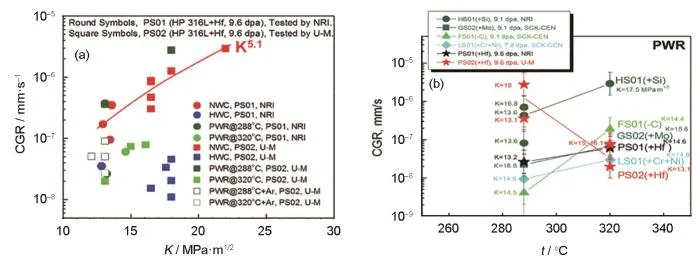
图2 IASCC数据中CGR随应力强度因子和辐照温度的变化规律[16]
Fig.2 Variation of CGR with stress intensity factor (K) (a) and irradiation temperature (b) in IASCC datas[16] (The matrix of samples with different numbers in the figure is high purity 316L stainless steel, and the contents in brackets represent the alloying elements adulterated or removed), The K dependence of the Hf addition alloy samples PS01 (round symbols) and PS02 (square symbols) irradiated to 9.6 dpa and tested in NWC, HWC, and PWR water CGR as a function of temperature for solute addition alloys tested at NRI, SCK-CEN, and U-M in PWR at 288oC and 320oC
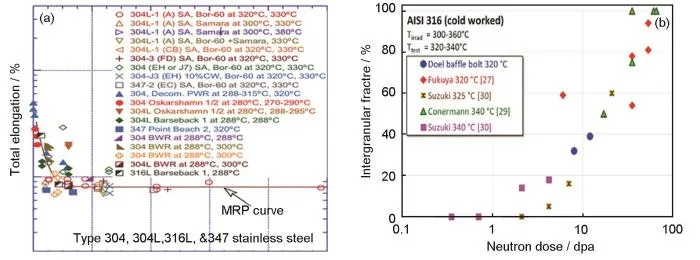
图3 中子辐照IASCC敏感性参数随剂量的变化[10,19]
Fig.3 Variation of IASCC sensitivity parameters with dose of neutron irradiation: (a) Yield strength and total elongation as a function of neutron dose for solution-annealed Type 304, 304L, 316L, and 347 stainless steels at 270-380oC[10], (b) Dose dependency of IASCC susceptibility of irradiated 316 stainless steel in a PWR environment with neutron exposure[19]
2 IASCC 机制研究
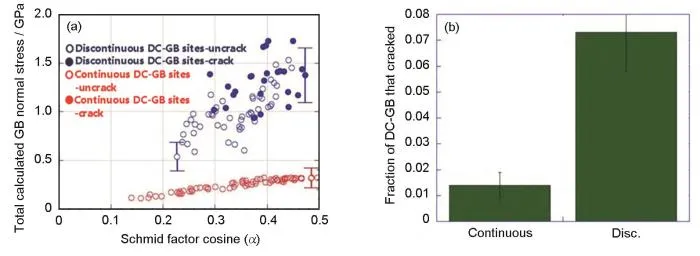
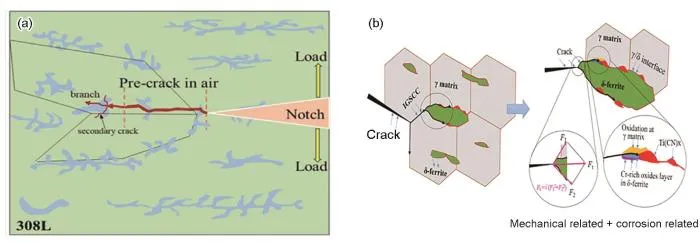
图4 DC-GB位置处的法向应力及开裂情况统计[23,24]
Fig.4 Statistics of normal stress and cracking at DC-GB position : (a) Total calculated stress acting normal to the grain boundary as a function of the crystallographic orientation of the deforming grain and the geometric orientation of the grain boundary normal vector[24], (b) Cracking statistics at different DC-GB locations[23]
图5 δ相对裂纹扩展的影响机理图[74]
Fig.5 Mechanism diagram of effect of δ phase on crack growth (a) Diagram of crack growth with network ferrite(b) Diagram of crack growth along the γ/δ phase boundary in the presence of Ti(CN) particles[74]
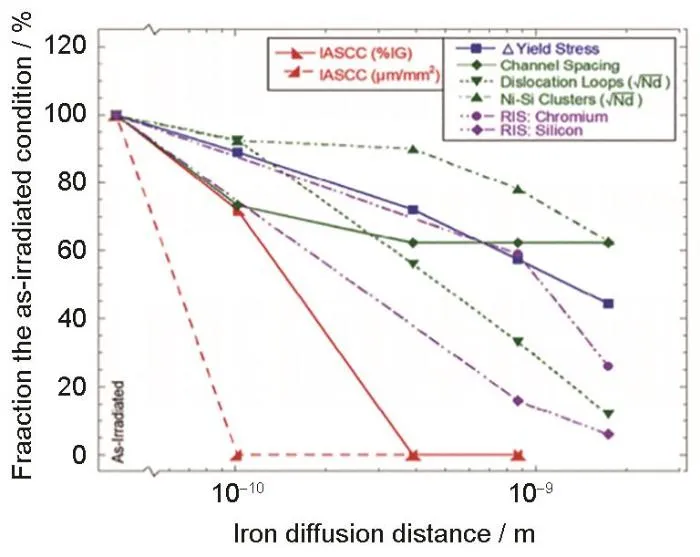
图6 IASCC敏感性和材料辐照诱导的特征随退火条件的变化图[86]
Fig.6 Plots of IASCC sensitivity and radiation-induced characteristics of the material as a function of annealing conditions (The five material states from left to right are: 5.9 dpa, 5.9 dpa + 500℃ annealing: 1 h and 5.9 dpa + 550℃ annealing: 1, 5, 20 h)[86]
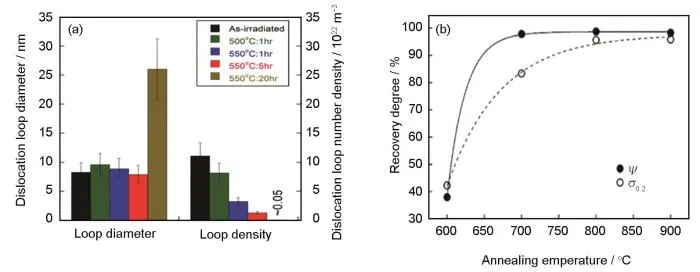
图7 微观缺陷与力学性能随退火条件的变化[79,85]
Fig.7 Variation of microscopic defects and mechanical properties with annealing conditions: (a) size and number density of dislocation loops in 304L stainless steel irradiated to 5.9 dpa under different annealing conditions[85], (b) recovery of yield strength (
) and ductility as a function of annealing temperature[79,85]
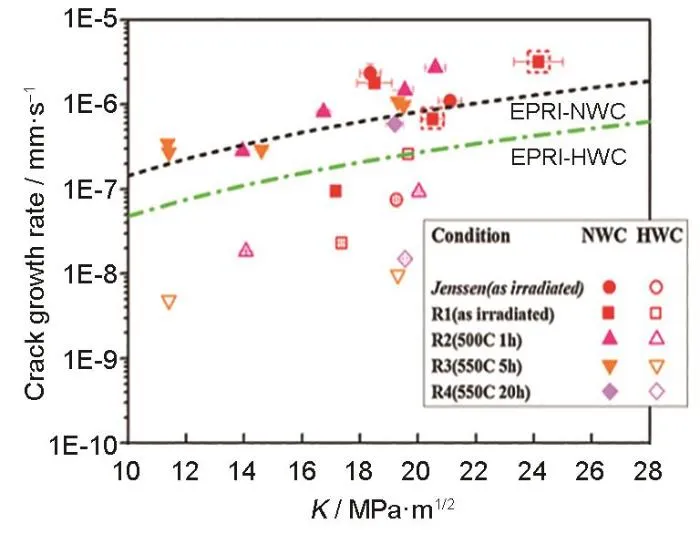
图8 辐照至5.9 dpa的304L不锈钢在不同退火条件和不同水环境下的裂纹扩展速率[54]
Fig.8 CGR of 304L stainless steel irradiated to 5.9 dpa under different annealing conditions and different water environments[54]
(Ni3Si)、G相、δ相、马氏体相以及α相的变化上,但马氏体与α相对IASCC的具体影响机制仍不明确。以上每种机制都可不同程度地促进或抑制IASCC。此外,PIA可以通过调节退火参数来一定程度上恢复辐照诱导产生的微结构与微化学变化,从而得出控制IASCC行为的主导机制。然而,由于实验样品稀缺,退火范围广泛,使得现有研究难以彻底分离辐照诱导的单一微观特征。
3 总结与展望
参考文献:
[1] Wang R S, Xu C L, Liu X B, et al. The studies of irradiation as‐ sisted stress corrosion cracking on reactor internals stainless steel under Xe irradiation [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2015, 457: 130
[2] Maksimkin O P, Tsai K V, Turubarova L G, et al. Void swelling of AISI 321 analog stainless steel irradiated at low dpa rates in the BN-350 reactor [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2007, 367-370: 990
[3] Jin H H, Shin C, Kim D H, et al. Irradiation induced dislocation loop and its influence on the hardening behavior of Fe-Cr alloys by an Fe ion irradiation [J]. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res., Sect., 2008, 266B: 4845
[4] Gupta J, Hure J, Tanguy B, et al. Evaluation of stress corrosion cracking of irradiated 304L stainless steel in PWR environment using heavy ion irradiation [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2016, 476: 82
[5] Jiao Z, Was G S. Impact of localized deformation on IASCC in austenitic stainless steels [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2011, 408: 246
[6] Jiao Z, Was G S. Localized deformation and IASCC initiation in austenitic stainless steels [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2008, 382: 203
[7] Gupta J, Hure J, Tanguy B, et al. Characterization of ion irradia‐ tion effects on the microstructure, hardness, deformation and crack initiation behavior of austenitic stainless steel: Heavy ions vs protons [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2018, 501: 45
[8] Andresen P L, Was G S. A historical perspective on understand‐ ing IASCC [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2019, 517: 380
[9] Kodama M, Nishimura S, Morisawa J, et al. Effects of fluence and dissolved oxygen on IASCC in austenitic stainless steels [A]. Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Envi‐ ronmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactor [C]. Monterey, 1991: 948
[10] Chopra O K, Rao A S. A review of irradiation effects on LWR core internal materials-IASCC susceptibility and crack growth rates of austenitic stainless steels [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2011, 409: 235
[11] Liang D S. Stress-based study on the initiation of stress corro‐ sion cracking of irradiated 304 stainless steel [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2020 ( 梁 迪 森 . 基 于 应 力 的 辐 照 304 不 锈 钢 应 力 腐 蚀 裂 纹 萌 生研究 [D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2020)
[12] Bosch R W, Vankeerberghen M, Gérard R, et al. Crack initiation testing of thimble tube material under PWR conditions to deter‐ mine a stress threshold for IASCC [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2015, 461: 112
[13] Ritter S, Horner D A, Bosch R W. Corrosion monitoring tech‐ niques for detection of crack initiation under simulated light wa‐ ter reactor conditions [J]. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol., 2012, 47: 251
[14] Ham J, Yoo S C, Lee Y, et al. Dissolved hydrogen concentration and proton irradiation effect on crack initiation behavior of 304L stainless steel [A]. Transactions of the Korean Nuclear Society Virtual Autumn Meeting [C]. Korean, 2021
[15] Eason E D, Pathania R, Jenssen A, et al. Technical basis part 2 for Code Case N-889: reference stress corrosion crack growth rate curves for irradiated austenitic stainless steels in light water reactor environments [J]. J. Pressure Vessel Technol., 2021, 143: 021202
[16] Ashida Y, Flick A, Andresen P L, et al. The key factors affect‐ ing crack growth behavior of neutron-irradiated austenitic alloys [A]. Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Envi‐ ronmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems— Water Reactors [C]. The Minerals, Metals, and Materials Soci‐ ety, USA, 2011: 1241
[17] Hashimoto T, Koshiishi M. Modification of the FRI crack growth model formulation from a mathematical viewpoint [J]. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol., 2009, 46: 295
[18] Rice J R, Drugan W J, Sham T L. Elastic-plastic analysis of growing cracks [A]. Proceedings of the 12th National Sympo‐ sium on Fracture Mechanics [C]. St. Louis, MO, 1980: 189
[19] Bosch R W, Van Renterghem W, Van Dyck S, et al. Microstruc‐ ture, mechanical properties and IASCC susceptibility of stainless steel baffle bolts after 30 years of operation in a PWR [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2021, 543:152615
[20] Deng P. Irradiation assisted corrosion and stress corrosion of nu‐ clear-grade 304 stainless steel in high temperature and high pres‐ sure water [D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2018 (邓 平 . 核级 304 不锈钢辐照促进高温高压水环境腐蚀与 应力腐蚀研究 [D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2018)
[21] Gupta J. Intergranular stress corrosion cracking of ion irradiated 304L stainless steel in PWR environment [D]. Toulouse: Université de Toulouse, 2016
[22] Fukuya K, Nishioka H, Fujii K, et al. Local strain distribution near grain boundaries under tensile stresses in highly irradiated SUS316 stainless steel [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2013, 432: 67
[23] McMurtrey M D, Was G S, Patrick L, et al. Relationship be‐ tween localized strain and irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking in an austenitic alloy [J]. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2011, 528A: 3730
[24] Johnson D C, Kuhr B, Farkas D, et al. Quantitative linkage be‐ tween the stress at dislocation channel–Grain boundary interac‐ tion sites and irradiation assisted stress corrosion crack initiation [J]. Acta Mater., 2019, 170: 166
[25] Deng P, Sun C, Peng Q J, et al. Study on irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking of nuclear grade 304 stainless steel [J]. Acta Metall. Sin., 2019, 55: 349 (邓 平, 孙 晨, 彭群家等 . 核用 304 不锈钢辐照促进应力 腐蚀开裂研究 [J]. 金属学报, 2019, 55: 349)
[26] Wang S H, Cai Z Y, Li M Z, et al. Numerical simulation on the local stress and local deformation in multi-point stretch forming process [J]. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol., 2012, 60: 901
[27] Du D H, Sun K, Was G S. Crack initiation of neutron-irradiated 304 L stainless steel in PWR primary water [J]. Corros. Sci., 2021, 193: 109902
[28] Swaminathan S, Sun K, Was G S. Decoupling the roles of grain boundary oxidation and stress in IASCC of neutron-irradiated 304L stainless steel [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2023, 585: 154604
[29] Moss T, Kuang W J, Was G S. Stress corrosion crack initiation in Alloy 690 in high temperature water [J]. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2018, 22: 16
[30] Scott P M. An overview of internal oxidation as a possible ex‐ planation of intergranular stress corrosion cracking of alloy 600 in PWRs [A]. BruemmerS, FordP, WasG. Ninth International Symposium on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nu‐ clear Power Systems- Water Reactors [M]. Newport Beach, Ca, USA:John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1999
[31] Kuang W J, Feng X Y, Du D H, et al. A high-resolution charac‐ terization of irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking of pro‐ ton-irradiated 316L stainless steel in simulated pressurized water reactor primary water [J]. Corros. Sci., 2022, 199: 110187
[32] Xie J Y, Zhang S H, Dong J Y, et al. Insights into the superior stress corrosion cracking resistance of FeCrAl alloy in high tem‐ perature hydrogenated water: the critical role of grain boundary oxidation [J]. Corros. Sci., 2022, 208: 110668
[33] Fujii K, Miura T, Nishioka H, et al. Degradation of grain bound‐ ary strength by oxidation in Alloy 600 [A]. Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems-Water Reactor [C]. The Minerals, Metals, and Materials Society, USA, 2011: 1447
[34] Dugdale H, Armstrong D E J, Tarleton E, et al. How oxidized grain boundaries fail [J]. Acta Mater., 2013, 61: 4707
[35] Stratulat A, Armstrong D E J, Roberts S G. Micro-mechanical measurement of fracture behaviour of individual grain boundar‐ ies in Ni alloy 600 exposed to a pressurized water reactor en‐ vironment [J]. Corros. Sci., 2016, 104: 9
[36] Fukumura T, Fukuya K, Fujii K, et al. Grain boundary oxidation of neutron irradiated stainless steels in simulated PWR water [A]. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Envi‐ ronmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems– Water Reactors [C]. The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series, USA, 2019
[37] Deng P, Peng Q J, Han E H. Grain boundary oxidation of pro‐ ton-irradiated nuclear grade stainless steel in simulated primary water of pressurized water reactor [J]. Sci. Rep., 2021, 11: 1371
[38] Deng P, Pen Q J, Han E H, et al. Study of irradiation damage in domestically fabricated nuclear grade stainless steel [J]. Acta Metall. Sin., 2017, 53: 1588 (邓 平, 彭群家, 韩恩厚等 . 国产核用不锈钢辐照损伤研 究 [J]. 金属学报, 2017, 53: 1588)
[39] Wang S K, Zhang S H, Xie J Y, et al. Clarifying the mitigation effect of proton irradiation on the intergranular oxidation of 316L stainless steel in high temperature water [J]. Acta Mater., 2022, 241: 118408
[40] Jacobs A J, Wozadlo G P, Gordon G M. Low-temperature an‐ nealing: a process to mitigate irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking [J]. Corrosion, 1995, 51: 731
[41] Deng P, Sun C, Peng Q J, et al. Review of stress corrosion cracking of structural materials in nuclear power plants [J]. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot., 2015, 35: 479 (邓 平, 孙 晨, 彭群家等 . 堆芯结构材料辐照促进应力腐 蚀开裂研究现状 [J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2015, 35: 479)
[42] Onchi T, Dohi K, Soneda N, et al. Mechanism of irradiation as‐ sisted stress corrosion crack initiation in thermally sensitized 304 stainless steel [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2005, 340: 219
[43] Bloom E E. Irradiation strengthening and embrittlement [A]. Conference on Radiation Damage in Metals [C]. Materials Park, OH, 1976: 295
[44] Grossbeck M L, Allen T R, Lott R G, et al. Effects of Radiation on Materials: The 21st International Symposium [M]. West Con‐ shohocken: ASTM International, USA, 2004: 92
[45] Hash M C, Busby J T, Was G S. The effect of hardening source in proton irradiation-assisted stress corrosion cracking of cold worked type 304 stainless steel [A]. Proceedings of the 21st In‐ ternational Symposium on Effects of Radiation on Materials [C]. Arizona, USA, 2004: 92
[46] Shoji T, Lu Z P, Murakami H. Formulating stress corrosion cracking growth rates by combination of crack tip mechanics and crack tip oxidation kinetics [J]. Corros. Sci., 2010, 52: 769
[47] Andresen P L, Ford F P. Life prediction by mechanistic model‐ ing and system monitoring of environmental cracking of iron and nickel alloys in aqueous systems [J]. Mater. Sci. Eng., 1988, 103A: 167
[48] Ford F P. Quantitative prediction of environmentally assisted cracking [J]. Corrosion, 1996, 52: 375
[49] Cui T M, Xu X H, Pan D, et al. Correlating oxidation resistance to stress corrosion cracking of 309L and 308L stainless steel claddings in simulated PWR primary water [J]. J. Nucl. Mater.,2022, 561: 153509
[50] Chen J J, Xiao Q, Lu Z P, et al. Characterization of interfacial reactions and oxide films on 316L stainless steel in various sim‐ ulated PWR primary water environments [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2017, 489: 137
[51] Bruemmer S M, Was G S. Microstructural and microchemical mechanisms controlling intergranular stress corrosion cracking in light-water-reactor systems [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 1994, 216: 348
[52] Bruemmer S M, Arey B W, Charlot L A. Influence of chromium depletion on intergranular stress corrosion cracking of 304 stain‐ less steel [J]. Corrosion, 1992, 48: 42
[53] Andresen P L, Morra M M. IGSCC of non-sensitized stainless steels in high temperature water [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2008, 383: 97
[54] Kuang W J, Hesterberg J, Was G S. The effect of post-irradia‐ tion annealing on the stress corrosion crack growth rate of neu‐ tron-irradiated 304L stainless steel in boiling water reactor envi‐ ronment [J]. Corros. Sci., 2019, 161: 108183
[55] Zhang K Q, Tang Z M, Hu S L, et al. Effect of cold work and slow strain rate on 321SS stress corrosion cracking in abnormal conditions of simulated PWR primary environment [J]. Nucl. Mater. Energy, 2019, 20: 100697
[56] Li G F, Kaneshima Y, Shoji T. Effects of impurities on environ‐ mentally assisted crack growth of solution-annealed austenitic steels in primary water at 325o C [J]. Corrosion, 2000, 56: 460
[57] Andresen P, Morra M. Effects of Si on SCC of irradiated and unirradiated stainless steel and nickel alloys [J]. Corrosion, 2005, 7
[58] Garner F A. Void swelling and irradiation creep in light water reactor (LWR) environments [A]. Tipping P G. Understanding and Mitigating Ageing in Nuclear Power Plants: Materials and Operational Aspects of Plant Life Management (Plim): A vol‐ ume in Woodhead Publishing Series in Energy [M]. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing, 2010: 308
[59] Was G S, Ashida Y, Andresen P L. Irradiation-assisted stress cor‐ rosion cracking [J]. Corros. Rev., 2011, 29: 7
[60] Lin X D, Peng Q J, Han E H, et al. Irradiation-induced precipi‐ tation and inverse coarsening of G-phase in austenitic stainless steel weld metal [J]. Mater. Charact., 2019, 151: 396
[61] Li Z B, Lo W Y, Chen Y R, et al. Irradiation response of delta ferrite in as-cast and thermally aged cast stainless steel [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2015, 466: 201
[62] Kumar P. Influence of microstructure on the corrosion behavior of a Ni-Si alloy [J]. MRS Online Proc. Library, 1984, 39: 537
[63] Liu C T, Oliver W C. Environmental embrittlement and grainboundary fracture in Ni3 Si [J]. Scr. Metall. Mater., 1991, 25:1933
[64] Brooks J A, Williams J C, Thompson A W. Microstructural ori‐ gin of the skeletal ferrite morphology of austenitic stainless steel welds [J]. Metall. Trans., 1983, 14A: 1271
[65] Brooks J A, Thompson A W. Microstructural development and solidification cracking susceptibility of austenitic stainless steel welds [J]. Int. Mater. Rev., 1991, 36: 16
[66] Lu Z P, Shoji T, Dan T C, et al. The effect of roll-processing orientation on stress corrosion cracking of warm-rolled 304L stainless steel in oxygenated and deoxygenated high temperature pure water [J]. Corros. Sci., 2010, 52: 2547
[67] Meng F J, Lu Z P, Shoji T, et al. Stress corrosion cracking of uni-directionally cold worked 316NG stainless steel in simulated PWR primary water with various dissolved hydrogen concentra‐ tions [J]. Corros. Sci., 2011, 53: 2558
[68] Terachi T, Fujii K, Arioka K. Microstructural characterization of SCC crack tip and oxide film for SUS 316 stainless steel in sim‐ ulated PWR primary water at 320o C [J]. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol., 2005, 42: 225
[69] Vankeerberghen M, Weyns G, Gavrilov S, et al. The electro‐ chemistry in 316SS crevices exposed to PWR-relevant condi‐ tions [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2009, 385: 517
[70] Sun B Z, Zhou X C, Li X R, et al. Stress corrosion cracking be‐ havior of 316L stainless steel with varying microstructure in am‐ monium chloride environment [J]. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot., 2021, 41: 811 (孙宝壮, 周霄骋, 李晓荣等 . 不同组织的 316L 不锈钢在 NH4 Cl 环境下应力腐蚀行为与机理 [J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学 报, 2021, 41: 811)
[71] Du D H, Wang J M, Chen K, et al. Environmentally assisted cracking of forged 316LN stainless steel and its weld in high temperature water [J]. Corros. Sci., 2019, 147: 69
[72] Manning P E, Duquette D J, Savage W F. Technical Note: the effect of retained ferrite on localized corrosion in duplex 304L stainless steel [J]. Weld. J., 1980, 59: 260-s
[73] Shalaby H M. Failure investigation of 321 stainless steel pipe to flange weld joint [J]. Eng. Fail. Anal., 2017, 80: 290
[74] Wang J M, Su H Z, Chen K, et al. Effect of δ -ferrite on the stress corrosion cracking behavior of 321 stainless steel [J]. Cor‐ ros. Sci., 2019, 158: 108079
[75] Pickering F B. Physical metallurgical development of stainless steels [A]. Proceedings of the Conference on Stainless Steels 84 [C]. Gothenburg, 1984: 2
[76] Aubrey L S, Wieser P F, Pollard W J, et al. Ferrite Measure‐ ment and Control in Cast Duplex Stainless Steels [M]. St. Lou‐ is, MO: ASTM International, USA, 1982
[77] Gao J X, Cao H, Zhong W H, et al. Effect of low dose irradia‐ tion of heavy ion on electrochemical corrosion and IASCC be‐ havior of austenitic steel [J]. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser, 2023, 2639: 1742
[78] Cao H, Gao J X, Yang W H, Liu C, Li D X, Zhang P, Zheng Q, Zhong W H. Effect of heavy ion irradiation on the electrochemi‐ cal behavior of 321 stainless steel [J]. NUCL. ENG. DES, 2024, 419: 112972
[79] Gurovich B A, Kuleshova E A, Frolov A S, et al. Investigation of high temperature annealing effectiveness for recovery of radi‐ ation-induced structural changes and properties of 18Cr-10Ni-Ti austenitic stainless steels [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2015, 465: 565
[80] Katsura R, Ishiyama Y, Yokota N, et al. Post-irradiation anneal‐ ing effects of austenitic stainless steels in IASCC [A]. Corrosion `98: Annual Conference and Exposition [C]. San Diego,1998: 311
[81] Fukuya K, Nakano M, Fujii K, et al. Separation of Microstruc‐ tural and microchemical effects in irradiation assisted stress cor‐ rosion cracking using post-irradiation annealing [J]. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol., 2004, 41: 1218
[82] Jacobs A J, Dumbill S. Effects of low-temperature annealing on the microstructure and grain boundary chemistry of irradiated type 304SS and correlations with IASCC [A]. 7th International Symposium on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nu‐ clear Power Systems-Water Reactors [C]. Breckenridge, 1995: 1021
[83] Van Renterghem W, Al Mazouzi A, Van Dyck S. Influence of post irradiation annealing on the mechanical properties and de‐ fect structure of AISI 304 steel [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2011, 413: 95
[84] van Renterghem W, Konstantinović M J, Vankeerberghen M. Evolution of the radiation-induced defect structure in 316 type stainless steel after post-irradiation annealing [J]. J. Nucl. Ma‐ ter., 2014, 452: 158
[85] Jiao Z, Hesterberg J, Was G S. Effect of post-irradiation anneal‐ ing on the irradiated microstructure of neutron-irradiated 304L stainless steel [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2018, 500: 220
[86] Hesterberg J, Jiao Z J, Was G S. Effects of post-irradiation an‐ nealing on the IASCC susceptibility of neutron-irradiated 304L stainless steel [J]. J. Nucl. Mater., 2019, 526: 151755
[87] Was G S. Localized deformation as a primary cause of irradia‐ tion assisted stress corrosion cracking [R]. Ann Arbor, MI (Unit‐ ed States): University of Michigan, 2009
免责声明:本网站所转载的文字、图片与视频资料版权归原创作者所有,如果涉及侵权,请第一时间联系本网删除。

官方微信
《腐蚀与防护网电子期刊》征订启事
- 投稿联系:编辑部
- 电话:010-62316606
- 邮箱:fsfhzy666@163.com
- 腐蚀与防护网官方QQ群:140808414